OLED technology has long been a new concept, but its recent upward trend is quite rapid. Various panel makers have invested heavily in new production lines. Market researchers say that OLED products will usher in a big explosion in the next few years. In the future, OLED is likely to replace the existing LCD technology, but whether it can dominate the rivers and lakes is still unknown, because there are many new display technologies waiting for it, Quantum Dot technology is one of them. Below we will make an in-depth analysis of the differences between the two technologies.
Technical difference analysis
First, let's review the differences in the working principles of the two technologies. OLEDs, as the name implies, rely on small LED arrays that can display different colors. Structurally, the LED in the OLED is made of an organic material, and also covers the phosphor layer, which can self-illuminate, so the technology eliminates the backlight layer on the conventional LCD. As long as the manufacturer fine-tunes the arrangement of the layers, different display effects can be obtained.
In contrast, quantum dot technology works in a completely different way. This technology relies not on LEDs, but on conductive crystals that are only 2 to 10 nanometers in diameter. These crystals can be combined with each other to show different colors through changes in crystal diameter, and their brightness can reach a fairly high level. However, the existing quantum dot screen still uses a blue LED backlight module, so the quantum dots act as a filter layer therein.
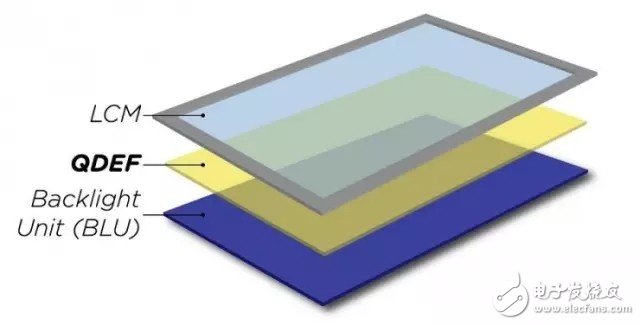
Although quantum dots can emit light, the industry is currently using it as a filter layer.
Color gamut and viewing angle competition
Compared with LCDs, OLEDs have a much wider color gamut, which gives consumers a better visual experience and color accuracy, so OLED screens have always been the darling of the media industry. Why is LCD so bad on these two items? Because the white backlight module used by it is not pure enough (blue LED is filtered by yellow phosphor layer to produce white light). However, the color point of the quantum dot is quite good, so the technician can directly filter the blue light into pure white light with the red-green filter, so that the defect of the LCD color difference is compensated.
By overcoming the inherent defects of LCD technology, the color compensation of the filter layer can be greatly reduced in the production process, so the brightness and color gamut of the quantum dot panel are greatly improved. In actual use, the color standard of the quantum dot panel can even exceed the OLED panel.
Manufacturing process and cost comparison
Of course, any comparison of cost throwing is a rogue, and the cost advantage is one of the important reasons why LCD is still active in the market.
Although the cost of OLED panels is declining with the development of technology, due to its complicated process and low yield, it is about 20% more expensive than LCD. However, with the advent of new technologies such as thermal foaming inkjet, the price of OLED panels will be two to three cheaper than LCDs in 2017.
However, due to the limited lifetime of the blue sub-pixels of the OLED panel, the phenomenon of "burning the screen" is likely to occur after a period of use. The quantum dot panel will not have such troubles, it works stably and has a long life.

In addition, due to the similar process, quantum dot screens also inherit the low-cost characteristics of LCDs, and the extra quantum dot filter layer at that level is very low cost. At the same size, quantum dot TVs cost only about $100 more than LCDs. If you switch to a 5-inch mobile device display, the cost increase is only about $10. However, maintaining the current cost level does not help the quantum dot panel to win. After all, the cost of OLED panels will become lower in the future.
In the future, quantum dot technology has the absolute strength to become a strong competitor of OLED, but now it is more like an improved version of LCD, rather than the successor of OLED technology. Of course, both have their own strengths and weaknesses, but quantum dot technology is constantly bridging the gap between the two. In the future, we will see more and more high-quality quantum dots and OLED panels appear. In the end, the market will give us the answer.
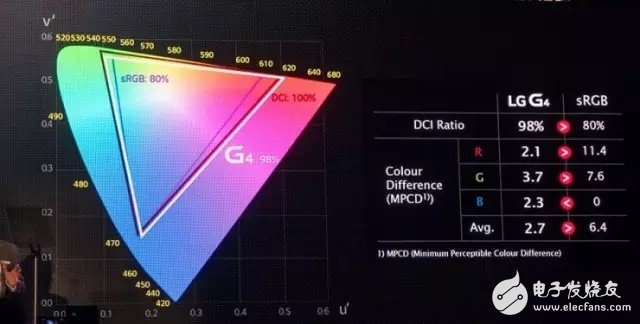
LG claims that the quantum dot screen color gamut of its flagship mobile phone G4 reaches 98%
However, since the backlight layer is not completely removed, the quantum dot panel is still not pure enough when it is displayed in black (the OLED screen can completely turn off the relevant sub-pixels when displaying a black screen), and the contrast cannot reach the top level. Therefore, OLED panels still have significant advantages in high contrast and high dynamic range scenarios.
The viewing angle of the LCD has always been a large slot. Unfortunately, the quantum dot panel that also uses the backlight module has not escaped this spell. Due to the presence of the filter layer, some light is scattered, so when the screen is viewed from the side, the screen is somewhat whitened. If the backlight layer cannot be completely removed, the viewing angle of the quantum dot panel cannot be significantly increased.
Vcsel Chip,Vcsel Laser Diodes,Round Laser Diode,Miter Saw Dual Laser
AcePhotonics Co.,Ltd. , https://www.cgphotonics.com