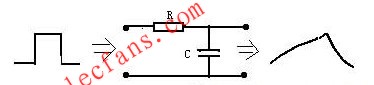
Differential circuit 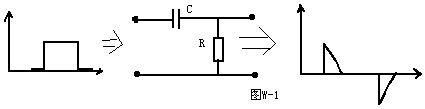
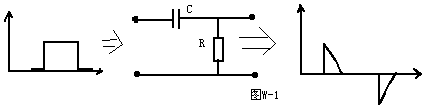
The circuit structure is shown in Figure W-1. The differential circuit can convert a rectangular wave into a sharp pulse wave. The output waveform of this circuit only reflects the abrupt part of the input waveform, that is, only the moment when the input waveform is abrupt. There is no output for the constant part. The width of the output spike waveform is related to R * C (that is, the time constant of the circuit). The smaller the R * C, the sharper the spike waveform, and vice versa. The R * C of this circuit must be far less than the width of the input waveform, otherwise it will lose the effect of waveform transformation and become a general RC coupling circuit. Generally, R * C is less than or equal to 1/10 of the width of the input waveform Okay.

Follow WeChat

Download Audiophile APP

Follow the audiophile class
related suggestion
At the moment of the rising edge of the input signal, because the voltage across C1 cannot be changed (at this time, the charging current is the largest, the voltage drops across the resistor R1), the output ...
The differential circuit—as the name suggests—can differentiate the signal, that is, a circuit that makes the output voltage proportional to the time rate of change of the input voltage. Differential circuit ...
The prerequisites of the integration circuit to form an integration circuit require the time constant of the integration circuit itself. The frequency cycle of the input signal, that is, C1 will not be charged during work ...
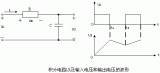
When the rectangular pulse is used as the excitation source of the RC series circuit, select a different time constant and output terminal, we can get some kind of output waveform we want, ...
A circuit whose output voltage is proportional to the rate of change of the input voltage is called a differential circuit. A simple RC differential circuit is to connect a capacitor after the input string and then connect an electric ...

The traditional differential amplifier has a differential gain of 96dB, a common input resistance of 500 megohms, a common mode rejection ratio of 106dB and more than 1 gigaohm ...
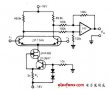
The circuit whose output voltage has a differential relationship with the input voltage is a differential circuit, usually composed of a capacitor and a resistor; the output voltage has an integral relationship with the input voltage ...
The circuit structure is shown in Figure W-1. The differential circuit can convert a rectangular wave into a sharp pulse wave. The output waveform of this circuit only reflects the sudden part of the input waveform, that is, only ...
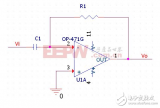
Practical differential circuit as shown in the figure is practical
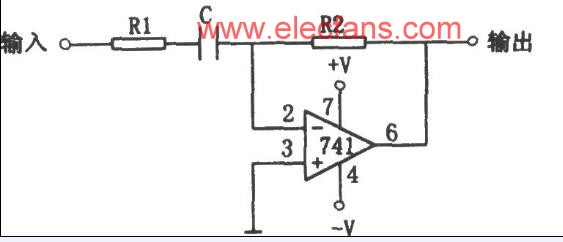
Functional differential circuits with strong anti-noise ability and practical differential circuits
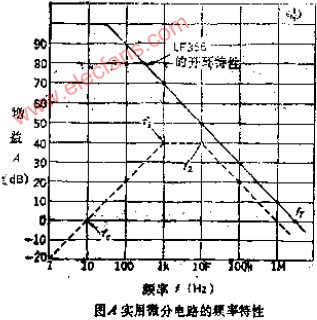
Practical Differential Circuit Basic differential circuit is only a principle differential circuit and cannot be put into practice
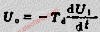
The basic differential circuit is that the differential circuit is the dual form of the integral circuit. In the basic integral circuit, the resistance of the input loop and the capacitance of the feedback loop ...
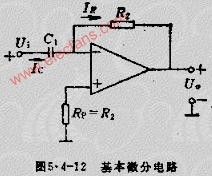
The acceleration circuit and its waveform acceleration capacitor C and the transistor input resistance R
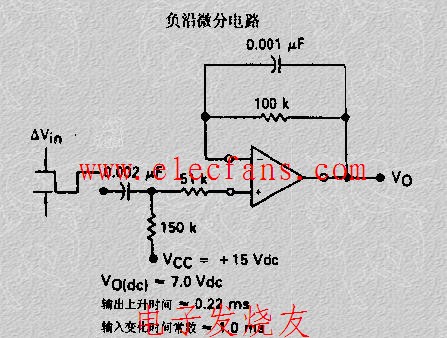
& nb