With the rapid development of the Internet, more and more information islands have already achieved Unicom. On this basis, achieving the Internet of Things is no longer a distant dream. Unconsciously, we have begun to contact the Internet of Things technology or even products in our lives.
Below, I will share with you some of the communication protocols in the IoT scene and hope to bring you more inspiration.
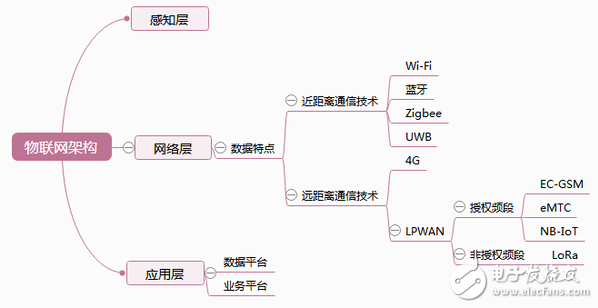
This article mind map overview
The basic architecture of the Internet of Things includes three levels: the perception layer, the network layer, and the application layer.
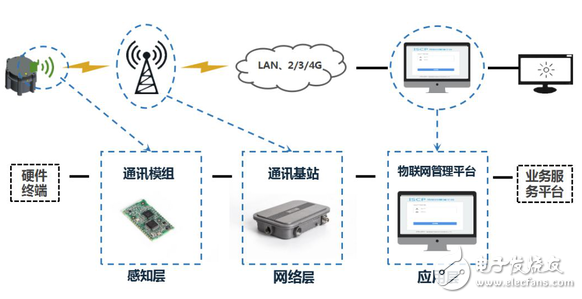
Internet of Things Architecture Diagram
The sensory layer collects certain data (acoustic, optical, electrical, etc.) through the sensor, and based on the terminal module of the network layer, it is connected to the base station at the network layer to implement data transmission after data acquisition.
The network layer is responsible for returning the data collected by the sensing layer, and it is very important to use different communication protocol technologies for backhaul based on different characteristics. This is the focus of this article.
The application layer can be understood as the data platform and service platform of the Internet of Things. The data platform serves as the aggregation point for all terminal data of the Internet of Things and is responsible for the unified storage and analysis of data. Northbound provides data invocation to the service platform through a standard API interface; the service platform implements various business logic based on the original data of the data platform. The service is presented.
Among them, focusing on the communication protocol at the network level is a battle for conquests and contending.
At present, the most popular Wi-Fi technology data transmission speed is fast, especially 802.11ax technology is about to be born. In theory, 8 streams are not dreams. However, as the speed increases, the power consumption increases sharply, and the transmission distance also becomes a problem. Long-distance transmission needs to place an AP at a certain distance for bridging, which will inevitably greatly increase the cost. Therefore, Wi-Fi technology is more suitable for indoor wireless Internet access scenarios for terminal applications such as PCs and PDAs.
Bluetooth technology and Wi-Fi have handovers on the 2.4G band, so there will be some interference problems in the same band. Bluetooth power consumption is slightly lower than Wi-Fi, and the transmission speed is far less than Wi-Fi. There are many applications in asset tracking, location tags, and medical sensors, such as smart watches, Bluetooth positioning, and more.
Zigbee technology has relatively small power consumption and relatively short communication distance. It is a short-range low-power technology and is mainly applied to wireless sensors and medical scenarios.
UWB UWB technology has a relatively clean frequency band and no interference from other frequency bands. It is more applicable in high-precision positioning scenarios.
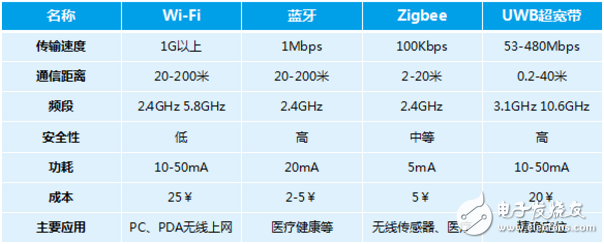
Communication protocol comparison
The above technologies are more suitable for the data transmission of short-distance scenes. What technologies are there in the long-distance scenario?
The 4G network provided by operators is the most widely used in people's lives and even exceeds Wi-Fi. It can do long-distance transmission, whether it is indoors or outdoors, the speed is very impressive. This kind of technology seems to be very advantageous, but its power consumption is large, and it can only be applied to the Internet of Things scenarios where terminals can collect electricity. For example, a company's shared bicycles use solar panels to take power.
In a long-distance scenario, if the terminal cannot solve the power supply problem, a technology with lower power consumption and greater coverage is needed to meet the IoT communication requirements in this scenario. So driven by business and technology, some experts and companies have developed a new type of communication technology, LPWAN, which is low-power wide area network technology, to solve this problem.
The goal of LPWAN is to provide long-distance wireless network communication technology optimized for M2M (device-to-device) communication scenarios in IoT applications. The advantages of LPWAN technology are mainly reflected in: low speed, ultra-low power consumption, long distance, low throughput, and strong coverage. These characteristics precisely indicate that this technology was developed for the long-distance transmission scenario of the Internet of Things. Specific applications such as: urban coverage, remote meter reading, manhole detection, and offshore fishing boat testing.
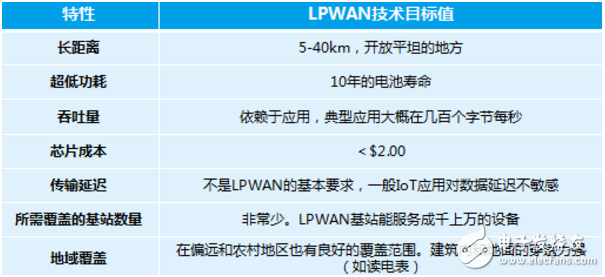
LPWAN Technical Features
As a new technology camp, LPWAN is divided into two major factions: licensed bands and unlicensed bands. The licensed band is further divided into EC-GSM, eMTC, and NB-IoT; the "top card" of the unlicensed band is LoRa.
EC-GSM
With the rise of LPWAN, the disadvantages of traditional GRPS applied to the Internet of Things become more obvious. In 2014, the 3GPP research project proposed migrating narrowband (200kHz) Internet of Things technologies to GSM, looking for a wider range of coverage than traditional GPRS by 20dB, and proposed five goals: to improve indoor coverage performance, support large-scale device connectivity, Reduce device complexity, reduce power consumption, and delay. In 2015, the TSG GERAN #67 conference report stated that EC-GSM has met five major goals. However, with the freeze of the R13 NB-IoT standard, people will devote more energy to the redefined standards.
eMTC
The concept of eMTC was formally named in R13. The former R12 is called Low-Cost MTC. It is an LTE-based Internet of Things technology. The eMTC is deployed based on a cellular network. User equipment can directly access the existing LTE network by supporting radio frequency and baseband bandwidth of 1.4 MHz. The key capabilities of the eMTC are high speed (compared to GPRS, zigbee, etc.), mobility, location, and voice support. .
NB-IoT
The recently hot NB-IoT is actually a fusion of both NB-CIoT and NB-LTE. NB-CIoT proposed a brand-new air interface technology, which is more changed than the traditional LTE network. He satisfies the five major goals of the TSG GERAN #67 conference. Its highlight is that the communication module costs less than the GSM and NB-LTE modules. The NB-LTE is compatible with the existing LTE, which is advantageous for deployment. After fierce debates, the two finally merged to form the technical standard of NB-IoT.
NB-IoT is called narrow-band Internet of Things and can be deployed directly on LTE networks. Good compatibility reduces deployment costs. Its own lower power consumption, theoretically estimated that the terminal module carrying NB-IoT based on the battery standby time up to 10 years. The reduction in the cost of the module also made it possible for more companies in the market to start applying this technology. This is one of the most popular ways to share a bicycle in the country. A company's third-generation smart lock adopts the NB-IoT module. On the one hand, it is the operator's vigorous promotion, and on the other hand it also brings value.
LoRa
It is LoRa which goes hand in hand with NB-IoT. The difference is that LoRa technology uses unlicensed bands. It is a super long-distance wireless transmission technology based on spread spectrum technology adopted and promoted by Semtech. LoRa stands for Long Range. As its name implies, LoRa can support long distance transmission. In China, LoRa can use two frequency bands: CN779-787 and CN470-CN510. Since the maximum emission power of CN779-787 is only 10dBm (10mW), there is no "practical" value. Therefore, people prefer the CN470-CN510 band, and its maximum transmit power can reach 17dBm (50mW).
Analogous to the Wi-Fi Alliance, LoRa also has a corresponding LoRa Alliance, which aims to establish standards and specifications together. LoRaWAN is such a product.
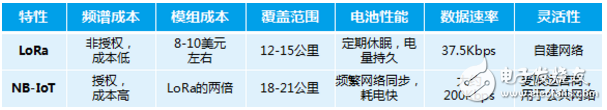
Comparison between LoRa and NB-IoT
Based on cost considerations, LoRa's module price is around 8-10 dollars, and the unlicensed band does not need to pay extra spectrum cost. Compared with NB-IoT, the cost has great advantages. In terms of battery performance, because NB-IoT works on licensed cellular spectrum, it needs regular network synchronization and consumes corresponding power, while LoRa has no such concerns, but this feature of NB-IoT is also warmly welcomed by shared bicycles. , based on this to do real-time vehicle positioning. In addition, from the business model point of view, NB-IoT belongs to the operator to build the network, the business side does not need to consider the deployment of the base station on their own, more peace of mind; but at the same time, the quality and security of the network are uncontrollable risks, and The value-added of the enterprise itself will also be hindered. In contrast, LoRa belongs to the enterprise self-built network. The base station needs to be deployed by itself. Follow-up needs its own operation and maintenance, optimization, etc. The dimensions of coverage, network quality and security must be responsible for themselves.
Up to now, no Internet of Things technology has become a true mainstream. There is no absolute perfection for the technology itself. Starting from the business, it is necessary to combine business characteristics and business models to choose a more appropriate IoT technology.
The development of the Internet of Things technology will be accompanied by the heroes of all parties. In the future, it will not be a tripartite effort or be dominated by new forces. Let us wait and see.
The above is related to the Internet of Things-IoT communication protocol disputes: related presentations for group competitions. If you want to learn more related information, please pay more attention to eeworld. eeworld electronic engineering will provide you with more complete, more detailed and updated information. information.
Litecoin (LTC) is a cryptocurrency created as a fork of Bitcoin in 2011. It uses a hashing algorithm called Scrypt that requires specifically designed mining software and hardware. It is minable, and continues to rank in the top cryptocurrencies for value and trading volume.
Litecoin mining is the process of validating transactions in the blockchain, closing the block, and opening a new one. Litecoin uses the proof-of-work consensus mechanism, which uses computational power to solve the nonce, which is part of the hash, that secures the block. The hash is the alphanumeric sequence of numbers that is encrypted by the hashing algorithm. When the nonce is solved, Litecoin is rewarded.
Litecoin mining became popular in 2011 when Charlie Lee, a software engineer at Google, announced its creation as a Bitcoin fork with modifications intended to help it scale more effectively.
Just like Bitcoin, it can be mined on computers using central processing units and graphics processing units. However, it isn't as profitable or competitive as purchasing an application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) and joining a mining pool.
Ltc Asic Miner,Antminer L3 Plus Plus,Bitmain Antminer L3 Plus,Bitmain L3 Plus
Shenzhen YLHM Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.ylhm-tech.com